iOS Crash Monitoring & Detection | Appxiom
Detect and fix app crashes in iOS with Appxiom. Catch errors early and see how crashes affect stability and user experience.
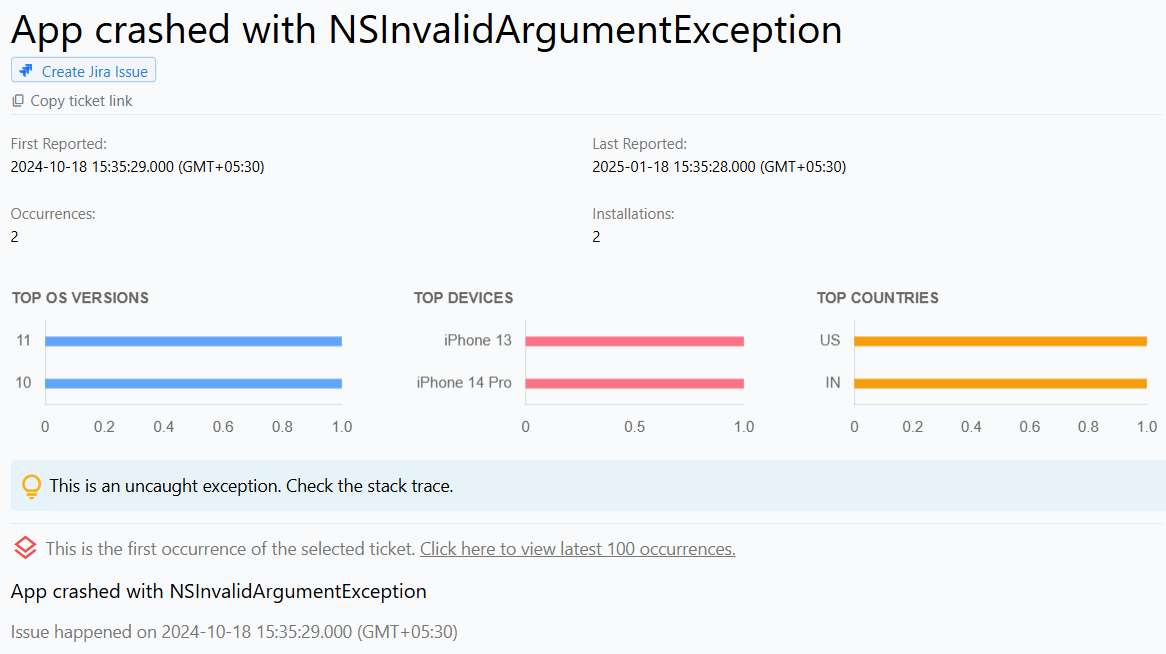
Detect iOS App Crashes
What Are Crashes in iOS and iPadOS Apps?
Crashes in iOS and iPadOS apps occur when an app unexpectedly terminates, causing it to stop functioning abruptly. These crashes can happen due to unhandled exceptions, memory problems, or other runtime errors.
When a crash occurs, users usually see a message indicating that the app has stopped working. They may have the option to force close the app or send a crash report to the developer. Frequent crashes can harm user experience, potentially causing data loss or disrupted app usage.
Reasons for Crashes in iOS and iPadOS Apps
Mach Exceptions: Low-level exceptions occur when a process attempts an illegal or unsupported operation, such as accessing protected memory or dividing by zero. Mach exceptions can lead to abrupt app termination.
Signals: Signals are software interrupts sent to a process when it encounters critical errors. iOS and iPadOS SDKs can detect signals like SIGSEGV (segmentation fault), SIGBUS (bus error), and SIGABRT (abort signal), which often result from memory access issues or programming errors.
Objective-C Exceptions: These exceptions happen when an object receives a message it cannot handle or when accessing a deallocated object. Detecting Objective-C exceptions is vital for proper iOS crash monitoring.
NSException: NSException represents higher-level exceptions in Objective-C. They occur due to invalid method calls, unhandled errors, or logic issues in the app. iOS error monitoring tools can capture NSException crashes, helping developers resolve them efficiently.
How to Use Crash Information to Fix iOS and iPadOS App Issues
Crash reports typically include the crash name, reason, and a stack trace. Developers can use this information for iOS error reporting to identify the root cause of the problem. By analyzing the stack trace, developers can implement fixes, improve app stability, and enhance the overall user experience.